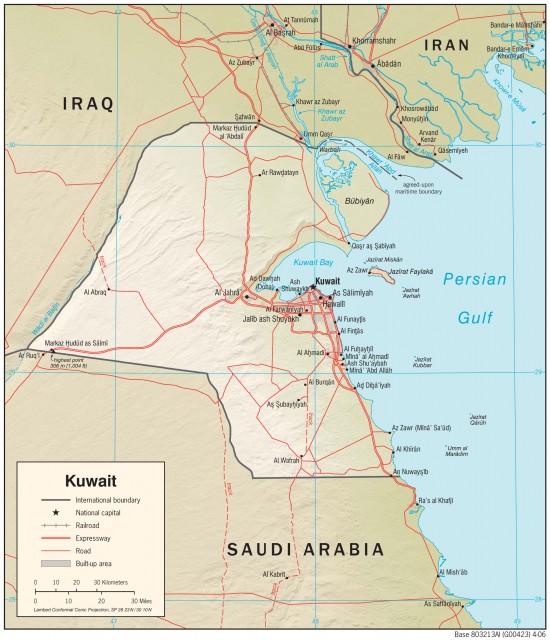
Kuwait
Area 6,880 square mi (17,280 square km)
Population 3.753 million 2014
Capital Kuwait City
Highest Point 1,004 ft (306 m)
Lowest Point 0 m
GDP $175.8 billion 2013
Primary Natural Resources petroleum, fish, shrimp, natural gas.
KUWAIT IS A COUNTRY in the MIDDLE EAST, bordering the PERSIAN GULF, between IRAQ and SAUDI ARABIA. The establishment of Kuwait took place in the 18th century by an Arab tribal group that came north from QATAR. They selected a defensible position at a prominent point on the southern edge of a broad bay near the outflow of the Euphrates River, at the head of the PERSIAN GULF.
Kuwait, as its place name implies in Arabic, began as a fortification near the water. The location provided a suitable point for transfer of goods to and from ships and liaison with the camel caravans of Arabia and Mesopotamia. Kuwait lay just on the margins of the OTTOMAN EMPIRE and acted as a trading center for goods entering or leaving the established routes serving that vast domain. In 1751, the Al Sabah family became the principal leaders of the small coastal commercial state. This ruling dynasty continues in a hereditary emirate type of government. As other gulf emirates before him, the Kuwait emir formalized relations with the BRITISH EMPIRE and became a protectorate by treaty in 1899.
UNIMAGINABLE WEALTH
Kuwaitis survived as traders and fishermen with meager wealth rising from the sea in the form of pearls. Oil was discovered in 1937 and once full exploitation began after World War II, unimaginable wealth began to rise from the desert. Kuwait quickly became a superrich oil country and developed a robust welfare state. On June 19, 1961, Kuwait became fully independent from Britain. The next 30 years saw continued development of the petroleum industry and massive wealth accumulation by the Kuwaiti government. Virtually every aspect of a citizen's life, education, health care, and housing was subsidized or provided for by the state government.
In 1990, neighboring Iraq used alleged theft of oil from a shared oil field as a pretext for invasion and annexation. Several United Nations (UN) resolutions demanded Iraq restore the Kuwait government and withdraw its troops. A UN-sponsored, U.S.-led coalition of nations established a large military force in Saudi Arabia. Once the UN-declared deadline of January 15, 1991, passed, coalition forces conducted an air and ground campaign that resulted in the liberation of Kuwait. Kuwait rapidly rebuilt its ransacked nation and reestablished oil production. Kuwait then became the staging area for U.S. and coalition forces, which maintained UN-mandated economic and military sanctions against Iraq for over a decade. In 2003, a U.S.-led coalition force launched a successful invasion of Iraq from Kuwait and other neighboring areas.
Kuwait's economy continues to be centered on the petroleum industry and the government sector. Its proven oil reserves account for about 10 percent of the world total. Kuwait's service and market sectors stand to benefit from the large-scale reconstruction and reorganization of the economy of Iraq. More than 90 percent of the population lives within the environs of Kuwait City and its harbor. An estimated 65 percent of the citizens of Kuwait, along with the royal family, belong to the Sunni branch of Islam.