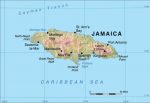
Natural Environment
Jamaica has a rich and varied natural environment. The island's land features range from low-lying coastal plains to the Blue Mountain crests reaching nearly 7,500 feet (2,286 meters) in elevation. Part of the island is a lush tropical paradise, and some areas are dry much of the year making them almost desertlike in appearance and […]
Andreas Schimper and Plant Adaptation to the Environment
Agriculture and commercial forestry have transformed the landscape over almost the whole of Europe. There are few areas of true wilderness remaining, and in an ecological sense the plant communities are not those that would have developed without human interference. Consequently, it is not easy to observe the way plants have adapted naturally to the […]
Ireland’s Physical Environment
Fado, fado, Ireland's geologic roots began with the formation of Western Europe. The island of Ireland today is a direct result of the earth-building forces that created Eurasia over two billion years ago. Over time, layers of sediment accumulated on the floor of ancient geologic seas, creating limestone. A mixture of this limestone and lava […]

Croatia: Physical Environment
In terms of its natural environment, Croatia is a tourist's dream come true. The country shares many similarities with California. Both are blessed with a very mild and pleasant Mediterranean climate. They both have long coastlines that rank among the world's most scenic. Each location has varied terrain, contributing to diverse landscapes and ecosystems. Unlike […]
Southeast Asia, Oceania, and Antarctica: Human–Environment Interaction
A HUMAN PERSPECTIVE In May 2000, the Smithsonian Institution honored Mau Piailug for preserving traditional navigation skills. Mau was born in Micronesia. When he was four years old, he began to sail with his grandfather, who taught the boy how to navigate without using instruments. Those methods of navigation were similar to those used by […]
East Asia: Human–Environment Interaction
A HUMAN PERSPECTIVE Hundreds of thousands of Chinese died in floods in the 20th century. Most of these deaths were caused by the flooding of the Chang Jiang and the Huang He rivers. These vast river floodplains are home to, and help feed, hundreds of millions of people, and this makes people vulnerable to the […]
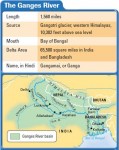
South Asia: Human–Environment Interaction
A HUMAN PERSPECTIVE Hinduism is the religion of most Indians. During one Hindu religious festival, millions of Indians gather near the city of Allahabad, where the Ganges and Yamuna rivers meet. A temporary tent city goes up, complete with markets, temples, and teahouses. People visit the market stalls and pray at the temples. They also […]
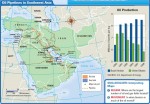
Southwest Asia: Human–Environment Interaction
A HUMAN PERSPECTIVE Icebergs for fresh water? As you have seen, fresh water is in short supply in Southwest Asia. In 1977, a Saudi prince, Muhammad ibn Faisal, formed a company to investigate the possibility of towing icebergs from Antarctica to the port of Jidda on the Red Sea. The icebergs would then be melted […]

Africa: Human–Environment Interaction
A HUMAN PERSPECTIVE Akierou Awe lives in a mud-brick house in Nigeria's Niger delta, a region that contains most of Nigeria's oil. On the morning of July 10, 2000, Awe's four sons had been collecting fuel from a leaking pipeline to help scrape out a living in this poverty-stricken region. They hoped to resell the […]
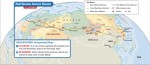
Russia and the Republics: Human-Environment Interaction
A HUMAN PERSPECTIVE Since the 1960s, irrigation policies in Central Asia have had a dramatic impact on the Aral Sea. A recent visitor to an old Aral fishing village described the change: “I stood on what had once been a seaside bluff . . . but I could see no water. The sea was twenty-five […]

Europe: Human–Environment Interaction
A HUMAN PERSPECTIVE “1800 DIE IN WIND-WHIPPED FLOOD WATERS!” February 1, 1953, witnessed a disaster in the Netherlands. Winds estimated at 110 to 115 miles per hour piled up gigantic waves that ripped through dikes—earthen banks—holding back the North Sea. When the storm was over, 4.5 percent of the Netherlands was flooded, and thousands of […]
Latin America: Human–Environment Interaction
A HUMAN PERSPECTIVE High in the Andes Mountains, in what is present-day Peru, the ancient Inca needed fields in which to grow crops. By the 1200s, in the highlands around their capital of Cuzco and elsewhere, the Inca carved terraces out of the steep sides of the Andes Mountains. They built irrigation channels to bring […]
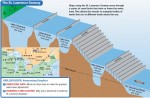
The United States and Canada: Human–Environment Interaction
A HUMAN PERSPECTIVE The sun-baked American Southwest was a harsh environment for its early inhabitants, the ancestors of today's Pueblo peoples. But these early settlers made good use of available resources. From the land, they took clay and stone building materials. They built multi-room, apartment-like dwellings in cliffs. This gave protection against daytime heat, nighttime […]
Natural Environments and Landscapes
France possesses a varied and productive physical environment. In this chapter, you will learn about the country's diverse land features, climates, soils, wild vegetation, and mineral resources. LANDFORMS Although considered a lowland country, France's physical geography is, in fact, extremely varied, ranging from high, rugged mountains to low-lying sandy coastal plains. Running northward and eastward through France is a major drainage […]
Global Change and Coastal Environments
Global climate change over the remainder of the twenty-first century will have major impacts on coastal environments. The changes include increases in seasurface temperature and sea level, decreases in sea-ice cover, and changes in salinity, wave climate, and ocean circulation. What changes have already occurred? According to recent reports of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, sea level has risen about 15 […]
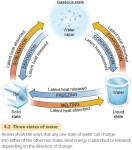
Water in the Environment
In this chapter, we focus on water in the air, both as vapor and as liquid and solid water. Precipitation is the fall of liquid or solid water from the atmosphere that reaches the Earth's land or ocean surface. It forms when moist air is cooled, causing water vapor to form liquid droplets or solid ice particles. If cooling is […]
Physical Geography, Environment, and Global Change
Physical geography is concerned with the natural world around us—in short, with the human environment. Because natural processes are constantly active, the Earth's environments are constantly changing. Sometimes the changes are slow and subtle, as when crustal plates move over geologic time to create continents and ocean basins. At other times, the changes are rapid, as when hurricane winds flatten vast areas […]
Geoarchaeology, Environmental History, and Causality
A very different intersection between anthropology and geography came about in the form of geoarchaeology, another integrative approach. Although geoscience applications to problems of dating, environmental reconstruction, and spatial organization in archaeology are common (mainly as 'archaeological geology'), and rapidly gaining in popularity, direct attention to the nature of the archaeological record is not. That record is a proxy for human […]
Contested Models of Agri-Environmental Governance
At the same time, agri environmental concerns have been swept into an increasingly international debate about the broad nature of agricultural sustainability and the role of farmers in delivering this. The restructuring and relocation of production that is likely within an increasingly globalized agro food system may prove as damaging to habitats and landscapes as earlier periods of agricultural change and […]
Developing an Environmentalist Critique of Modern Agriculture
Environmentalist critiques of modern farming first emerged in places like Western Europe, the United States, and Canada during the late 1970s. Mounting evidence of the biodiversity, soil erosion, and off farm pollution impacts of agricultural intensification and specialization was brought to public attention by campaigning scientists and journalists and by conservation groups in both the EU and North America. In the […]
Agri-Environmentalism and Rural Change
The realization that modern, intensive agriculture could be environmentally damaging was slow to gain ground among policy elites in industrialized countries. Traditionally portrayed as environmental stewards engaged in the production of essential staples, farmers in most developed countries since the 1930s have received substantial levels of government support in order to achieve food security and public good policy goals. […]
Environmental Geographies of the Sea
Just as historically there has been little cultural geography of the sea, similarly few human geographers until recently have focused on the ocean as a space of nature. To some extent, this likely is because, until recently, it was believed that humans could do little to influence the condition of the marine environment or the status of marine resources. Prior […]

Negotiating Environments
Some of the earliest geographical research, which engaged with older peoples' changing relationships with environments, drew heavily on environmental psychology published in the 1960s and 1970s, and in particular on the pathbreaking work of gerontologist Powel Lawton. Lawton's ecological theory of aging was most famously articulated through his environmental docility hypothesis (also associated with terms such as aging and […]

human-environment relationships
THE ENVIRONMENTAL approach in geography, history, anthropology, psychology, and other spheres of humanitarian thought remains one of the most alluring and unequivocal since its origin in ancient times. At the beginning of the 21st century, interdisciplinary studies of cultural history using contemporary methods of instrumental analysis are often bringing scientists to the necessity of taking […]