Guam (USA)
AT A GLANCE
Capital: Hagatna (Agana)
Size: 209 sq. mi. (541 sq km)
Population: 162,742(2016)
Government: Unincorporated territory of United States
Electoral votes: 0
U.S. Representatives: 1 (nonvoting)
THE PLACE
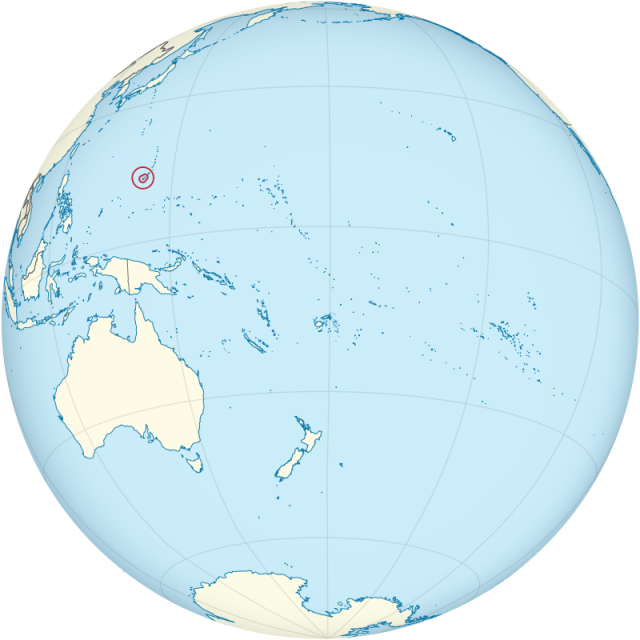
Guam is located in the Pacific Ocean at the southern end of the Mariana Islands. It lies about 1,300 miles (2,100 km) east of the Philippines in an area known as Micronesia.
Guam has many coral reefs, as well as a mountain range formed by volcanoes in the south. The northern part of the island consists of a limestone plateau. Guam's largest town is Tamuning, and Apra Harbor is the island's chief port.
Typhoons, or devastating ocean storms, often strike the island, and earthquakes occur occasionally. Guam's climate is warm year-round and especially rainy from May to November.
THE PAST
Chamorros, or groups from Southeast Asia, were the first known people to migrate to Guam, arriving sometime before 1500 B.C. Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan was the first European to arrive in Guam, in 1521. Spain claimed Guam in 1565 but did not actively govern it until 1668. After Spain lost the Spanish-American War in 1898, it gave up Guam to the United States and sold the Northern Mariana Islands to Germany.
The U.S. Navy was responsible for handling Guam's affairs until the Japanese took it over in 1941, during World War II. The United States reclaimed Guam in August 1944. In 1950, when the United States made Guam a territory and transferred control to the U.S. Department of the Interior, Guam's residents became U.S. citizens.
In 1954, the U.S. military used about one-third of Guam's land to build Andersen Air Force Base. Guam first elected its own governor in 1970, and in 1972, sent a delegate to the U.S. House of Representatives. Guam's representative can vote in committees but not in general House floor votes.
THE PRESENT
Tourism and related industries produce the largest part of Guam's income. More than 500,000 tourists, mostly from Japan, visit Guam each year.
The United States has a strong presence in Guam, and the U.S. military is Guam's second-largest source of income. About one-sixth of Guam's workforce is employed by the U.S. military.
Agriculture and fishing are minor economic activities. Coconuts, sweet potatoes, taro, and tuna are the most common agricultural and fish products of Guam.