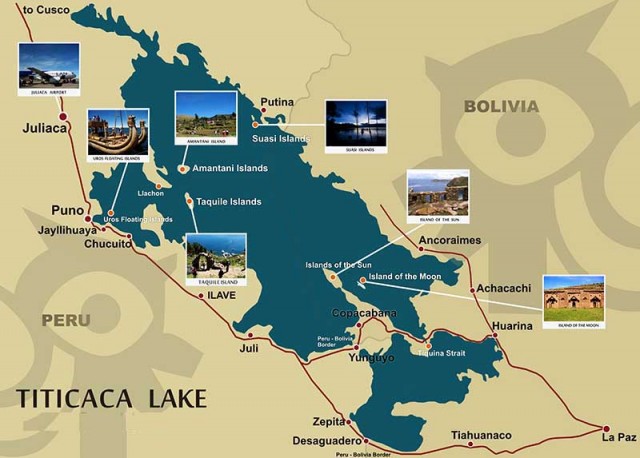
Titicaca, Lake
HIGH IN THE ANDES MOUNTAINS between BOLIVIA and PERU at 12,580 ft (3,810 m) above sea level, Lake Titicaca is said to be the highest fresh-water lake on Earth navigated by large vessels. Forty-one islands, some of them densely populated, rise from its shores. The lake covers 3,200 square mi (8,300 square km) and extends in a northwest-to-southeast direction for 120 mi (190 km). It is 50 mi (80 km) across at its widest point and divided at its narrowest point by Tiquina Strait. The southeast portion of the lake is called Lago Huinaymarca in Bolivia and Lago Pequeno in Peru. A larger section in the northwest is called Lago Chucuito on the Bolivian side and Lago Grande in Peru. Titicaca's depth averages between 460 to 600 ft (140 and 180 m) with the greatest recorded depth, 920 ft (280 m), in the northeast corner.
The origin and meaning of the name Titicaca is uncertain. Ruins along the lake include a temple on Titicaca Island marking the spot where, according to legend, the founders of the Inca Empire, Manco Capac and Mama Ocllo, emerged from the waters, sent to Earth by the sun. Legend also has it that when Spanish Conquistadors in search of gold reached Cuzco, the retreating Incas reportedly took a two-ton gold chain from the temple at Koricancha and threw it into Titicaca. Attempts to find it have been unfruitful although underwater ruins of an inundated, ancient city have been discovered.
DISPUTED CLAIMS
Is Titicaca the largest lake in South America? VENEZUELA's Lake Maracaibo is larger at 5,100 square mi (13,210 square km). Is Titicaca the highest lake in the world and is another oft-repeated claim true that Titicaca is the highest navigable lake in the world? Lake Namtso in TIBET (15, 479 ft or 4,718 m above sea level) is crossed daily by boats. Yamdrok in CHINA (14,570 ft or 4,441 m above sea level) is navigated by shepherds who ferry their flocks across its waters. Is Titicaca the highest freshwater lake in the world? More than 20 rivers flow in, but only the Desaguadero River drains at the lake's southern end. Most of the water is lost by evaporation. As a result, Titicaca's waters are slightly brackish, with salinity ranging from 5.2 to 5.5 parts per 1,000 and measurable quantities of sodium chloride, sodium sulfate, calcium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate.
In 1862 the first steamer to ply the lake was disassembled in England and carried on muleback up to the lake. Large vessels make regular crossings from Puno, Peru, to the Bolivian port of Guaqui. A narrow-gauge railway connects Guaqui with La Paz, Bolivia. The world's second-highest railway runs from Puno down to Arequipa, Peru, and the PACIFIC OCEAN.