Turkey
Area 301,384 square mi (780,580 square km)
Population 75.93 million 2014
Capital Ankara
Highest Point 16,945 ft (5,166 m)
Lowest Point 0 m
GDP $798.4 billion 2014
Primary Natural Resources antimony, barite, coal, copper, emery.
TURKEY IS A NEAR Middle Eastern country located in northwestern Asia with a toehold in extreme southeastern Europe. It is about the size of TEXAS and LOUISIANA combined. About 3 percent of Turkey's land area is in Europe. Thrace, its European area, is about the size of VERMONT at 9,412 square mi (24,378 square km). Its Asian area (Asia Minor) is called Anatolia and covers 291,971 square mi (756,202 square km). Turkey's coastline is 2,211 mi (3,558 km) long.
Turkey's eastern border is shared with IRAN, AZERBAIJAN, ARMENIA, and GEORGIA. Its Anatolian northern border is on the BLACK SEA. Its Thracian territory borders BULGARIA and GREECE on the north. Its western coast lies on the AEGEAN SEA facing Greek islands. The western part of the southern border is its MEDITERRANEAN SEA coast until it meets the Asian mainland. The center of its southern border is shared with SYRIA. The eastern part of its southern borders is shared with IRAQ.
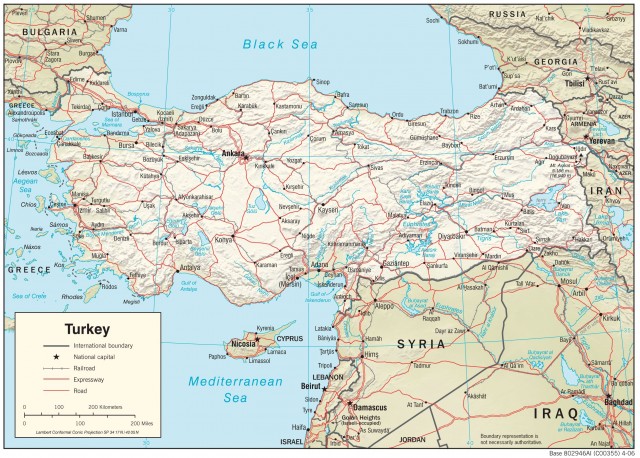
Turkey has seven major regions: the Black Sea region, the Marmara region, the Aegean, the Mediterranean, Central Anatolia, East Anatolia, and Southeast Anatolia. The Black Sea region extends from the Bosporus Strait to Georgia. The Northern Plains run along the western half of the Black Sea coast in a narrow belt until the Northern Mountains meet the Pontic Mountains.
PONTIC MOUNTAINS
The Northern Mountains cover a large area in of northwestern Asiatic Turkey. They meet the Pontic Mountains about midway along the Black Sea coast. The Northern Plains then continue along the Pontic Coast of the Black Sea to the border with Georgia. In some areas the mountains come all the way to the coast. The Northern and Pontic Mountains receive enough moisture for them to be heavily wooded. There are only a few roads through the Pontic Mountains to the Black Sea.
The Thracian part of the Marmara region is covered by the Northern Plains, an area of gentle rolling grass lands and farms. Historic ISTANBUL (Constantinople) is located in European Turkey on a peninsula at the intersection of the Bosporus and the Sea of Marmara. An estuary called the Golden Horn separates it from newer areas. In addition, Istanbul has expanded across the Bosporus to the Asian side. European Turkey is separated from Asiatic Turkey by three connected waterways: the Bosporus Strait, the Sea of Marmara, and the Dardanelles.
The Bosporus Strait, one of the world's busiest waterways, is a narrow outlet from the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara. It is only a few hundred yards wide at its narrowest point. The Sea of Marmara is a saltwater sea but almost completely surrounded by land. It opens onto the Dardanelles, which is a strait formed by the Gallipoli Peninsula and the Northern Plains. The Island of Marmara in the Sea of Marmara is an important source of high-quality marble. The Northern Plains also extend along the Asiatic side of the Sea of Marmara, and beside the Dardanelles, they open onto the Aegean Sea.
The Aegean coast has many bays, peninsulas, coves, islands and fine sandy beaches. Its narrow coastal plains rise through the broad fertile Western Valleys to the Anatolian plateau. The Western Valleys produce numerous agricultural products, including olives, tobacco, and cereal grains. They contain the Gediz Plain and the Great Menderes Plain where grapes, figs, and citrus are grown.
The sea changes from the Aegean off the Island of Rhodes to the Mediterranean. The southern Mediterranean coast has a narrow belt of plains, the Southern Plains, that run from the Gulf of Antalya to the border with Syria. Rising just inland are the Southern Mountains, the most important of which are the Taurus Mountains (Toros Daglari). They are a folded chain of mountains.
The Taurus range runs eastward until it reaches the Arabian Platform, where it arcs around the northern side of the platform. The Taurus Mountains are rugged and have historically been a barrier to travel between the Mediterranean coast and the Anatolian Plateau except for a few mountain passes such as the Cilician Gates (Gulek Bogazi), northwest of Adana (Tarus).
The Central ANATOLIAN PLATEAU is a region of a small rivers fed by only occasional rainfall. Without irrigation the land is usually just grazed by herding. There are several salt lakes in central Turkey. It contains the volcanic tuff region of Cappadocia in the south, an area larger than RHODE ISLAND that has strangely shaped rock formations.
The Eastern Anatolian Plateau region is an area of rugged towering mountains. The area lies east of the Euphrates River and extends to Mount Ararat and the borders with Armenia and Iran. It also contains the large freshwater body, Lake Van, which is part of the original homeland of the Armenians. The Southeastern Anatolian region is part of Mesopotamia. It is a region of fertile plains and river valleys that lie between Turkey's share of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers. The Euphrates rises near Erzurum in the Eastern Plateau. The Tigris rises in the Taurus Mountains near Lake Hazer in the Eastern Plateau.
Numerous Kurds live beyond the Tigris River in the Eastern Plateau in extreme southeast Turkey along its borders with Iraq and Iran. The Anatolian Plateau was an important part of Hittite, Armenian, Persian, Roman, Hellenistic, and Byzantine empires. Since its conquest by the Ottoman Turks in the Middle Ages, it has been the home to the Ottoman Empire and to modern Turkey.