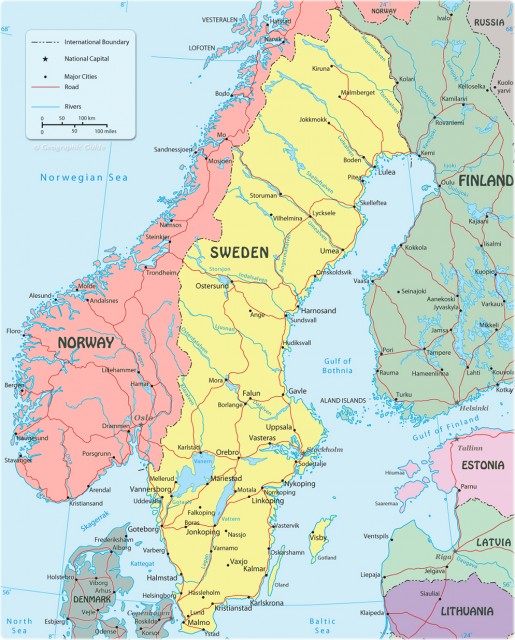
Sweden
Area 173,732 square mi (499,964 square km)
Capital Stockholm
Population 9.690 million 2014
Highest Point 6,024 ft (2,111 m)
Lowest Point 0 m
GDP $571.1 billion 2014
Primary Natural Resources zinc, iron ore, lead, copper, silver, timber.
SWEDEN IS ONE of the four Scandinavian countries of northern Europe. Like its neighbors NORWAY and FINLAND, Sweden is a long country from south to north, encompassing climatic variation from the relatively temperate south to subarctic areas north of the ARCTIC CIRCLE. The majority of the Swedish population is concentrated in the far south, across the straits from Denmark, leaving the rest of Sweden mostly empty. One of the key features of Sweden is its wilderness, with forests covering over half of the country.
In a country with an area slightly larger than CALIFORNIA but a population five times smaller, Swedes have always cherished individual space and freedom. This has evolved into the traditional Swedish characteristic respect for individual rights and for the environment. This character, combined with the stability derived from a complete lack of warfare, internal or external, since the beginning of the 19th century, has created a modern society with one of the strongest economies in Europe and the best social welfare system in the world.
Sweden shares a long border with Norway along the mountainous spine of the Scandinavian Mountains. To the east, Sweden has a long coastline along the Baltic Sea and the Gulf of Bothnia. Most of Sweden's many rivers flow east from the mountains down to the sea. Several of these rivers pass through long, narrow lakes that are marks of the retreating glaciers from the last ice age. Some of the larger such glacial depressions are now filled with large lakes, notably Sweden's largest, Vanern, and Vattern, in the south-central part of the country. Where another of these lakes, Malaren, meets the Baltic, it has formed a large archipelago, on which is built the city of Stockholm. Sweden also has two large, mostly flat islands in the Baltic, Gotland and Oland. Besides Stockholm, there are two other large cities: Goteborg and Malmo.
Sweden's 21 counties, or lan, can also be grouped into historic provinces—Vasterbotten, Norrland, Skane, Svealand, and Gotaland. The last two of these older provincial names reflect the names of some of the original tribes who eventually merged to form the Swedish nation: the Svears and the Goths. These northern Germanic peoples were known as the Vikings in their heyday of the 9th to 11th centuries. A single kingdom was forged in the Middle Ages and remained in relative obscurity until the 17th century, Sweden's golden age, when the kingdom extended its control across the Baltic, including Finland, ESTONIA, LATVIA, and the northern coasts of POLAND and GERMANY.
Swedes even entered the Atlantic trade market, establishing colonies in the Caribbean (present-day St. Barthelemy) and North America (today's DELAWARE). Low population and limited raw materials, however, could not support a large empire, and by the end of the 18th century, the Swedish empire had collapsed. Finland was lost to Russia in 1809 but compensated for by Norway in 1814, though the two countries were virtually independent until the actual separation of Norway from Sweden in 1905.
Since then, Sweden has transformed itself from a poor agricultural nation to one of the industrial powerhouses of Europe, mostly through high-quality export products. Swedish machinery and technology and other products are famous throughout the world: famous brands include Volvo, Saab, Ericsson, IKEA, H&M, and Absolut. Much of this “Swedish economic miracle” was achieved by using Sweden's enormous wealth of forests, ore and hydroelectric power. Information technology and biomedicine are two areas in which the Swedes are leading in new global markets. Swedes are willing to cooperate with their neighbors but also guard their independence and neutrality. They are not members of the NORTH ATLANTIC TREATY ORGANIZATION (NATO), they delayed entry into the EUROPEAN UNION (EU) until 1995, and they opted not to adopt the euro currency in 1999. Globally, Sweden is a leader of the nonaligned nations and works to export its own peaceful character to the rest of the world through United Nations organizations and the famous Nobel Peace Prize.