Syria
Area 71,498 square mi (185,180 square km)
Population 22.16 million 2014
Capital Damascus
Highest Point 9,232 ft (2,814 m)
Lowest Point -656 ft (-200 m)
GDP $40.41 billion 2007
Primary Natural Resources oil, gas, phosphates, asphalt.
THE SYRIAN ARAB Republic (“Al-Jumhria Al-Arabia Al-Suria” in Arabic) is a Middle Eastern country located at the southwestern edge of the Asian continent. On the west it borders the MEDITERRANEAN SEA; TURKEY on the north; IRAQ on the east and southeast; JORDAN and ISRAEL on the south; and LEBANON on the southwest.
The Syrian Arab Republic (SAR) is usually called by the ancient name of Syria (“Sham”). Its two major regions, the western and eastern regions, are separated by the Great Rift Valley (Jordan Trench). Within these regions are mountains, plains, and valleys.
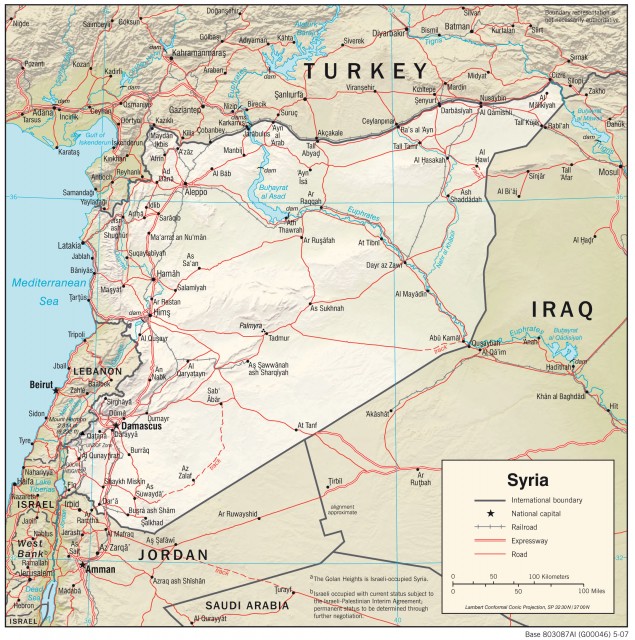
The western region lies on the western side of the Great Rift Valley. Its features are the coast, mountains, and river valleys. The coast is a narrow strip of land that runs along the Mediterranean Sea from Lebanon to Turkey. The coast is an important agricultural region that receives enough moisture from the Mediterranean Sea so that irrigation is not necessary. In the south, the Plain of Akkar extends across the border with Lebanon.
Along the coast are sandy beaches alternating with rocky headlands and cliffs. These are spurs of the Jabal an Nusayriyah (Jabal Alawite) range, which runs roughly north and south.
The Great Rift Valley divides Syria's eastern and western regions. The Jordan River rises on Mount Hermon and flows south in the Jordan Trench to the Sea of Galilee. The rift valley then continues north to near the border with Turkey. Its northern end is near Aleppo (Haleb), one of Syria's major cities. The Orontes River flows north in the rift valley (Ghab Depression) along the eastern side of the Jabal an Nusayriah range through the cities of Homs, Hama, and Apamea before turning west to flow to Latakia on the coast. The fertile Orontes Valley is home to much of Syria's population.
The Anti-Lebanon Mountains (Qalamun Sinnir) form the eastern edge of the rift valley. They contain Mount Hermon. Damascus is east of them at an oasis nourished by the Barada River. The Anti-Lebanon Mountains run roughly northward to near Homs before angling sharply to the northeast as the Palmyra range (Jabal Abu Rujmayn and finally as Jabal Bishri). The Palmyra range is a mountainous area about 3,000 ft (910 m) high that stands above the central part of the plateau. In the north many deep wadis descend from the plateau to the Euphrates.
The Euphrates River rises in Turkey and flows across Syria before entering Iraq. The Tabka Dam on the Euphrates has formed the Assad Reservoir. Further downstream, the Balikh and Khabur rivers also join the Euphrates as they flow across the Al-Jazirah (upper Mesopotamia) region.
The GOLAN HEIGHTS are a mountain plateau area in southwestern Syria overlooking the Sea of Galilee. Israel currently occupies the area. Eastward is the Jabal ad Duruz in the extreme south of the country. This mountain area is home to the Druze, a secretive Shiite sect of Islam. It is also the source of the Yarmuk River. It crosses southern Syria and part of Jordan before joining the Jordan River. The southern and eastern areas of Syria are the northern part of the Syrian Desert.
This area is located on a plateau that descends from 2,000 to 3,000 ft (610 to 910 m) above sea level at the edge of the rift valley. It gradually descends to a flat sandy desert plain that joins with the border of Iraq. It also slopes down to the Euphrates River as its eastern boundary. Much of the southern part is a rocky plain. Syria, as part of the FERTILE CRESCENt, contains numerous historic places. One is the ruin of Palmyra, which was a famous caravan city on the Spice Road.