El Nino and La Nina
EL NINO AND La Nina are parts of global weather systems that recur every two to seven years. An El Nino, which usually lasts 12 to 18 months, is characterized by warm winters and wet springs in North America, a lessening of monsoonal rains in Asia, and droughts affecting Africa and the south PACIFIC OCEAN. A La Nina system follows for up to three years, producing opposite effects.
Southern Oscillation indicates the variations in sea level pressure noted in the Pacific between the southern and northern hemispheres. Both El Nino's and La Nina's are considered part of the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO), a term used to describe the full range of wind and ocean patterns reflected in the Southern Oscillation itself. An El Nino occurs when the northeast tradewinds of the south Pacific slacken, and in the same area, ocean water warms and moves east. This action can reverse the trade winds by causing an increase in warm air, which rises and changes air pressure patterns. Abnormally dry weather then settles over islands in the tropical Pacific like INDONESIA, BORNEO, and the PHILIPPINES, while humid, warm air affects the west coast of South America.
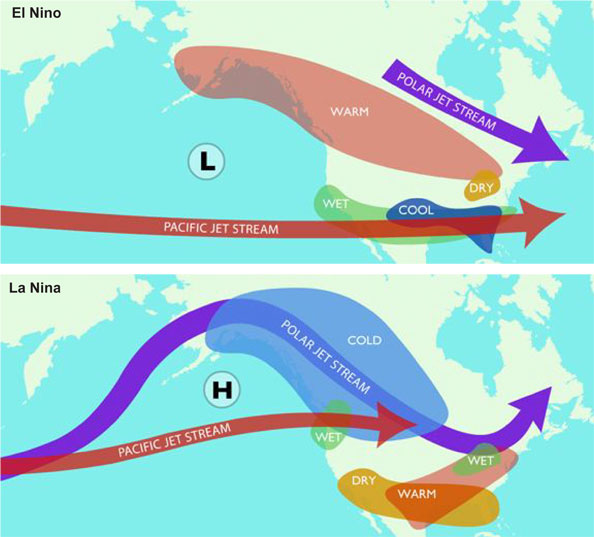
Over several months, an El Nino impacts world weather patterns. In winter, the U.S. Pacific northwest and western CANADA get less rain, while southern CALIFORNIA and the Gulf Coast experience more rain and storms. Also in the UNITED STATES, warmer temperatures affect the Great Plains and upper midwest. BRAZIL, southern Africa, and AUSTRALIA experience dryness and drought. Rainfall lessens and drought often hits INDIA and southern Asia. Monsoonal moisture, a critical element on which all farmers depend, may not arrive, and the result is famine, often followed by diseases and death. Fewer hurricanes develop in the ATLANTIC OCEAN, and less rain falls in MEXICO and the southwestern UNITED STATES. In the Pacific Ocean, more typhoons occur.
Clearly, aberrations in the weather can cause great hardship and loss of life. The loss of monsoon rains in India for several years in the 1890s caused a famine that claimed over 4 million lives. An El Nino brings other troubles as well: Abnormal ocean temperatures keep fish from shore, ruining coastal economies. Normally dry high altitudes get snow, and months later when the snow melts, mudslides and flooding can follow. Huge brush fires, sparked in unusually dry conditions, can devastate large areas; in 1997 and 1998, fires in Indonesia caused at least $9 billion in damage and lost timber, as well as dramatically polluting the air throughout Southeast Asia to such an extreme extent that the sun could not be seen for days in some cities. Even when the fires were extinguished, underground peat continued to burn, contributing to the pollution.
An El Nino is typically, but not always, followed by a year or more of La Nina conditions. During La Nina, also called an El Viejo, the temperatures in the equatorial Pacific region are colder than normal. This results in wet winter weather in the South Pacific and southern Asia, and drier conditions along the South American coast. In the United States, winter temperatures are warmer in the southeast and cooler in the northwest.
The history of the ENSO goes back thousands of years, but it was not identified until recently. In 1891, the president of the Lima Geographical Society first officially reported that fishermen in PERU sometimes noted a warm countercurrent in the Pacific Ocean right after Christmas that indicated more rain, exotic fish, and lots of vegetation would come the following year. The locals called it El Nino, a term referring to the Christ child. Although droughts, floods, and seasons of unusual weather had been noted and even studied for years, it was not until the 1920s that scientist Gilbert Walker identified the Southern Oscillation. In the 1960s, Norwegian meteorologist Jacob Bjerknes connected Walker's discovery with the extensive ocean warming of an El Nino system. He described the anomalous circulation patterns that followed, and named them the Walker Circulation.
Scientists, historians, archaeologists, and researchers all over the world are now putting events and data together, realizing that weather systems such as the ENSO last for years and have impacted civilizations on a global scale for millennia. Events once considered random and unrelated are now being explained in terms of climatic events. El Nino droughts were likely responsible for the downfall of the Mayan civilization in Central America, the Moche Empire of Peru, and the Anasazi complex of the American southwest. Glacial ice cores, coral reefs, and tree rings provide evidence of ancient weather patterns and anomalies.
The El Nino of 1997–98 was one of the worst in recent memory. The fires of Indonesia have been mentioned; large economic losses impacted many areas, such as Australia and Southeast Asia, where drought occurred. Ironically, this El Nino came with much advance warning, and areas like heavily populated California were able to invest millions of dollars in preparation, thus avoiding more losses.
Groups such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) predict and track El Ninos using satellites, research ships, buoy arrays, computer modeling, and other tools to analyze ocean temperatures, wind speeds, fish populations, precipitation, and other early indicators of developing weather systems.